DVB - T
Digital Video Broadcasting – Terrestrial

DVB - T
DVB-T is an abbreviation for "Digital Video Broadcasting — Terrestrial"; it is the DVB European-based consortium standard for the broadcast transmission of digital terrestrial television that was first published in 1997 and first broadcast in the UK in 1998. This system transmits compressed digital audio, digital video and other data in an MPEG transport stream, using coded orthogonal frequency-division multiplexing (COFDM or OFDM) modulation. It is also the format widely used worldwide (including North America) for Electronic News Gathering for transmission of video and audio from a mobile newsgathering vehicle to a central receive point. [1]
Flowgraph
FOr the test we implemented a flowgraph. This flowgraph uses the SDR boards, which were provided, for the communication. [3]
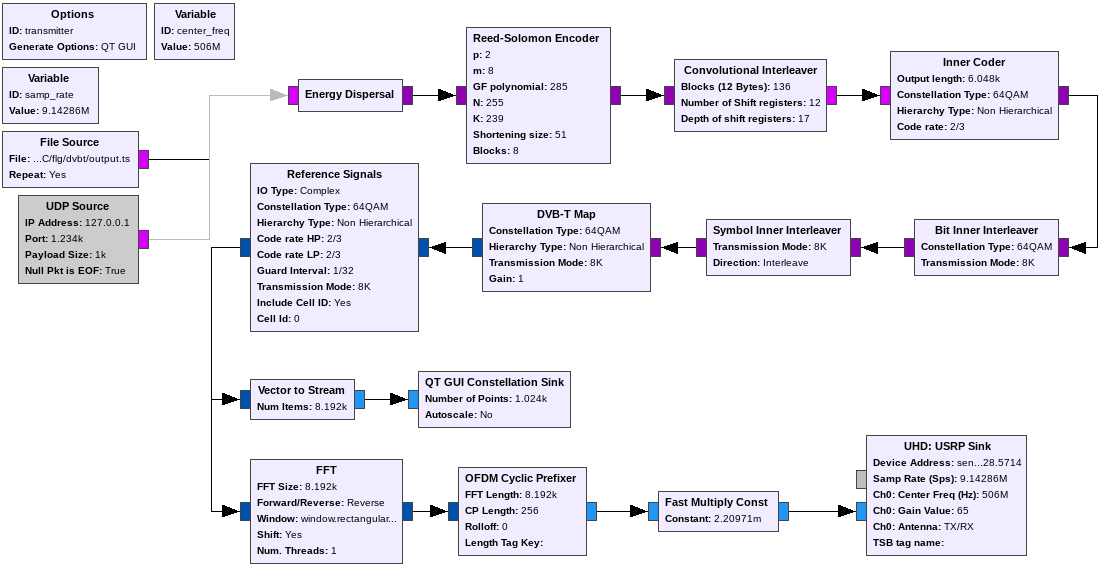
The flowgraph used for the test can be downloaded here: dvbt_tx.grc
FFmpeg
FFmpeg is an open-source video and audio transformation tool, which was uesd to convert an
arbitrary
input video into a DVB-T compliant vido stream.
Usage for DVB-T conform conversion
ffmpeg -i <input_file> -vcodec mpeg2video -s 1020x1080 -r 29.97 -b:v 24M -minrate:v 24M -maxrate:v 24M -bufsize:v 1.4M -acodec mp2 -ac 2 -b:a 192k -t 60 -f mpegts outfile.ts
Description of Used Options
The options used for the convertion are described in this chapter. [2]
- -vcodec
- sets the videocodec. For DVB-T the MPEG-2 (mpeg2video) codec is used. MPEG-2 is a lossy video compression and lossy audio compression standard.
- -s
- sets the frame size
- -r
- sets the frame rate
- -b:v
- sets the average video bitrate
- -minrate:v
- sets the minimum bitrate tolerance to be used
- -maxrate:v
- sets the maximum bitrate tolerance
- -acodec
- sets the audio codec
- -ac
- sets the number of audio channels.
- -b:a
- sets the audio bitrate
- -t
- limits the duration of data read from the input file in seconds
- -f
- sets the output file format. MPEG-TS is a container format for transmission and storage of audio and vido. MPEG-TS was designed for less reliable transmission such as terrestrial or satellite broadcast. The container format encapsulates packets of an elementary audio and video stream with error correction and synchronization features for maintaining transmission quality when the communication channel carrying the stream is degraded.
Available bit rates (Mbit/s) for a DVB-T system in 8 MHz channels
This chapter shows a table with the available bit rates for the DVB - T transmission. [1]
| Modulation | Coderate | Guard Interval | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1/4 | 1/8 | 1/16 | 1/32 | ||
| 64-QAM | 1/2 | 14,929 | 16,588 | 17,564 | 18,096 |
| 2/3 | 19,906 | 22,118 | 23,419 | 24,128 | |
| 3/4 | 22,394 | 24,882 | 26,346 | 27,144 | |
| 5/6 | 24,882 | 27,647 | 29,273 | 30,160 | |
| 7/8 | 26,126 | 29,029 | 30,737 | 31,668 | |